How would you react if you knew that someone was reading sensitive information you sent over the Internet without your knowledge? Unauthorized third parties do this all the time, monitoring how victims communicate with loved ones, banks, and even their employers. Known as man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, they have become more common than you might think.
Below, we'll fill you in on what man-in-the-middle attacks are, how they're carried out, and what you can do to protect yourself.
What Are Man in the Middle Attacks?
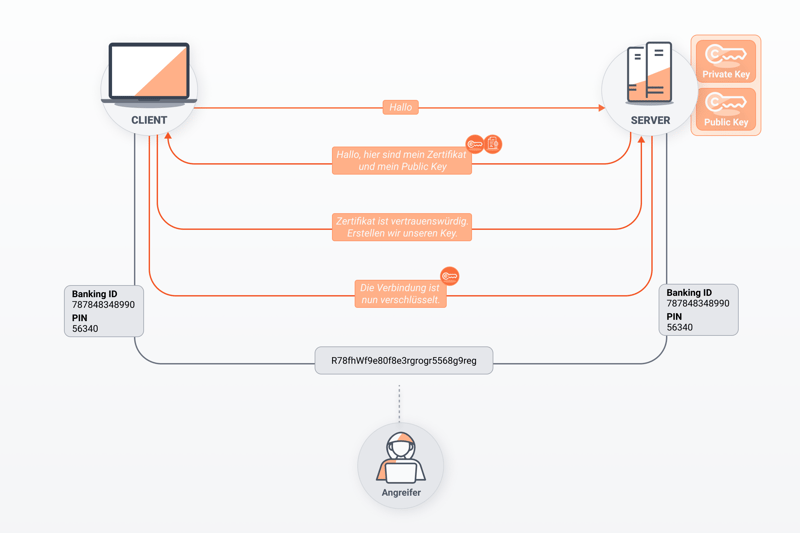
A man-in-the-middle attack occurs when online communications are monitored without the victim's knowledge. The attacker positions themself between the victim's computer or device and the resource they're trying to access online, like a website. MITM attackers are able to acquire sensitive information like usernames and passwords thanks to security gaps or weaknesses in how their device communicates with the Internet.
Generally, MITM attacks can be broken down into two phases: First, data is captured, and then it is decrypted.
In order to 'catch' your data, the attacker must convince both parties (for example, your computer, and the server of the website that you're attempting to access) that you're directly communicating with one another. Of course, since the attacker is in the middle, they need to make it seem that they're not. After that, the attacker needs to decrypt the data that they've captured to make it usable.
Types of Man in the Middle Attacks
There are many weak points that cybercriminals can exploit for different kinds of MITM attacks. Often, spoofing plays a role. This is a kind of manipulation in which something is presented differently than what it actually is.
Below, we've summarized the various kinds of MITM attacks:
DNS spoofing
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the Internet's phonebook, converting domain names into IP addresses so that browsers can load requested resources (websites). This process goes faster if the domain name has already been translated and is stored in the browser cache. In DNS spoofing, MITM attackers use this cache to gain access to the DNS server and modify a website's address entry.HTTPS spoofing
HTTPS is a secure communication protocol for data transfers between browsers and servers. When HTTPS is spoofed, attackers use fake security certificates which are accepted by browsers. During these attacks, even though you and your computer think the website you're visiting is safe, it actually isn't, allowing hackers to decrypt your data.IP spoofing
With this, hackers change the IP address of a website to direct traffic elsewhere. Users believe that they're on a legitimate website when in reality, hackers are following their every move.ARP spoofing
Address Resolution Protocols are responsible for discovering MAC addresses on local networks. If spoofed, hackers can connect a user's IP address to a spoofed MAC address, allowing them to catch any data that the former might send.Rogue access point
Access points are what devices use to connect to wireless networks. Rogue access points, on the other hand, are malicious, appearing legitimate, but actually monitoring all data traffic.Session hijacking
During session hijacking, a MITM attacker locks real users out of a web session (such as logging in to an application) by stealing the legitimate user's session token. In this way, hackers can access and use your account as though they were you, getting away with as much sensitive information or money as they like.
The above is just a selection of the most prevalent kinds of man-in-the-middle attacks, and unfortunately, there are plenty of others. For example, hackers can install malware in your web browser (referred to as a man-in-the-browser attack). Similarly, emails can be intercepted in order to monitor your banking behavior.
As such, the sky is the limit when it comes to methods and exploits, making it almost impossible to guard against all of them. For that reason, the more important question is how to recognize and prevent MITM attacks.
How to Recognize a Man in the Middle Attack?
Unfortunately, it can be very difficult to recognize a man-in-the-middle attack while it's ongoing. Still, some indications include:
Disrupted connections & long loading times: Frequent connection disruptions and longer than usual loading times are two possible signs that a MITM attack is going on. Of course, these can just mean that the network you've connected to is having issues, or that your ISP is doing maintenance.
Loss of HTTPS encryption: Whenever an HTTPS address in your browser changes to an unencrypted HTTP one, there's a strong possibility that a MITM attack is underway.
Don't expect to be able to identify a MITM attack as it's happening. Instead, invest your efforts in prevention and minimizing risk, since there's a lot you can do.
9 Ways to Protect Against Man in the Middle Attacks
Bad news first: There's no such thing as 100% protection against malicious middlemen. Still, there are a number of steps you can take to make yourself as hard a target as possible. Most hackers look for 'easy' marks and won't waste their time on tougher opponents. Accordingly, we identified 9 measures you can take to counter the threat of MITM attacks.
Pay Attention to a Website's Encryption
Websites that lack adequate encryption are particularly susceptible to MITM attacks. In technical terms, we're talking about HTTP connections that don't have Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption.
For that reason, make sure that you only visit HTTPS websites. Your browser will usually alert you when visiting unencrypted websites anyways.
HTTPS websites are secured with SSL certificates.
Safe Routers
Powerful and up-to-date encryption is also important on routers. For these, WiFi Protected Access (WPA) has become the standard. Along with ensuring that your router has adequate encryption, check that its firmware is current and that your router's login data and WiFi password are regularly changed.
Be Cautious on Public WiFi
Whether in a Starbucks or at the airport: Lots of MITM attacks are orchestrated on public WiFi since these don't have the protection afforded by home or corporate networks. When connected to a publicly accessible network, be extra careful (especially when visiting unencrypted HTTP websites). To enhance your defenses, you can use a VPN, which we'll discuss below.
Say No to Email Phishing
This one prevents all sorts of nasty cyber surprises: Don't open suspicious emails, and if you do, definitely do not click on or download any links or attachments. The same goes for messages that look like they might have come from your bank, favorite online marketplace, or social media network asking you to submit your login details or other sensitive information. They will never request them from you via email or over the phone.
Watch Your Passwords
The more accounts you have, the more passwords you'll need. To make these as effective as possible keep the following in mind:
- 1.
Create secure passwords. These should include at least eight numbers and special characters.
- 2.
Don't recycle passwords. Each account you have needs its own unique password. This prevents password thieves from using the same password to gain access to other accounts associated with your email address.
- 3.
Change your passwords regularly.
If you have lots of accounts, it might feel impossible to guarantee adequate security for all of your passwords without some help. Password managers don't only remember all of your passwords for you, giving you access to them with one master password, they'll also let you know when your passwords should be changed, and help to create new ones.
Activate Multi-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication, also known as multi-factor authentication, gives your accounts added security. With it, a password isn't enough to gain access to your accounts, as a second factor (such as clicking on a link in an email or inputting a code from an authenticator app) is needed.
This complicates matters for data thieves, as they need to also have access to the second factor in order to pry open your account.
Encrypt Your Communications
Whether email, video (i.e. Zoom or Google Meet), or just chatting (WhatsApp, Signal, etc.), make sure your online communications always have end-to-end encryption. This guarantees that your messages arrive encrypted to your recipient, and only they can decrypt them. No one - whether admins on the platform you're using or malicious hackers - can sneak a peek while these are in transit.
Use a Firewall and Antivirus Software
Installing a firewall and antivirus software enhances your protection against all sorts of cyberattacks, including man-in-the-middle ones. Make sure that your antivirus software and its definitions are up to date since clever cybercriminals are always stepping up their game.
Use a Reliable VPN
A virtual private network (VPN) is also a middleman, but the good kind. These route your data traffic to remote servers, masking your IP address, and encrypting your connection in the process. Direct contact between your device and the Internet is minimized, which comes in particularly handy when using public WiFi.
VPN services like NordVPN automatically encrypt your Internet connection.
However, make sure that you only use legitimate VPN services, since you're putting your data in their hands. Unfortunately, there do exist lots of shady (free) VPN services that can and do keep tabs on what their users are up to. This makes them just like man-in-the-middle attackers. For this reason, stick with reputable providers that regularly submit to independent security audits.
In our EXPERTE.com VPN comparison, we put a wide variety of VPNs to the test. Reviews and more can be found in the VPN section of our site:
Conclusion
Man-in-the-middle attacks are dangerous and difficult to notice. Cybercriminals disguise themselves as reputable intermediaries, stealing sensitive data like passwords when your system is transmitting them to a trusted web resource. This is made possible by weaknesses in digital infrastructure and communications through DNS, IP, or HTTPS spoofing, to say nothing of malware.
Noticing a man-in-the-middle attack while it's happening is hard. For that reason, it's smarter to implement security practices that will reduce the likelihood of an MITM attack occurring. When surfing, make sure you do so with HTTPS encryption, and if on public WiFi, exercise added caution.
You aren't alone though, as a number of useful tools exist that can enhance your safety. For maximum password security, there's no way around a password manager; antivirus programs and firewalls can boost your digital defenses; and if you often find yourself on public WiFi, you might want to invest in a reliable VPN.
FAQs
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks occur when someone positions themself between your system and the Internet resource you're trying to communicate with. They then steal sensitive data like passwords, that you might transmit to the (legitimate) Web service. There are many different types of MITM attacks, with DNS spoofing, HTTPS spoofing, IP spoofing, Rogue Access Points, and session hijacking common.
Identifying a MITM attack is difficult. Should the attacker use DNS spoofing, you might notice odd-looking or incorrect URLs (such as www.expere.com instead of www.experte.com). HTTPS URLs that suddenly transform into HTTP URLs are another likely indicator of a MITM attack. Beyond that, other potential warning signs are abnormal connectivity issues and slower loading times.
There's no such thing as 100% protection. To reduce your vulnerability to MITM and other cyberattacks, there are a number of proactive measures you can take. Surf only when HTTPS encryption is available, be careful on public WiFi, and don't open suspicious emails from people you don't know. For more support, you can use password managers, VPNs, and antivirus software.