When using the Internet, you reveal a lot of information about yourself. One example is your IP address, which is unique and identifies both your router and gives away your location. In this article, we'll let you know about the different kinds of IP addresses and when it makes sense to conceal them.
What Is an IP?
An Internet Protocol (IP) address identifies devices on a network, whether at home or on the World Wide Web. Like a phone number, IP addresses are a unique combination of numbers, which makes it possible to link them to a single device. Whenever you visit a website, its servers will see your router's IP address. This isn't an invasion of your privacy: It lets those servers know where they need to send the data packets you've requested.
A public IPv4 IP address typically looks like this:
104.26.5.112
A public IPv6 IP address is a bit longer:
3A52:9109:7DC0:6774:7238:7746:DD5F:8B9A
Below, we'll explain what IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses are. There are other types of IPs too, namely:
Public and private IP addresses;
Static and dynamic IP addresses
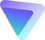
Public vs. Private IP Addresses
Devices like smartphones, tablets, printers, and PCs connect to the Internet via a router. This serves as a gateway between network participants (you, your friends, your family, etc.) and the World Wide Web. However, some devices might have private IP addresses, making them uniquely identifiable on the network. These addresses are assigned by the router so that it knows where a request originated from.
One of the most commonly-used private IP addresses is 192.168.0.0. This sequence of numbers is not random: The first part, 192.168.0 (24-bit) comprises what is known as the Network ID, which will be the same for all network participants. The second part (8 bits) is the Host ID and identifies the device. This can range from 0 to 255, but in the example above, is 0.
Unlike a public IP address, private IPs don't have to be unique, since they're only used on a home network and won't provide access to the Internet. The number of possible combinations (65,536) makes it possible to identify all connected devices, even on large corporate networks.
A router generates and assigns a private IP address according to three factors:
Number sequence | Network size | Composition | |
|---|---|---|---|
Area A | 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 | For large networks | 8 bits for the network and 24 for the host |
Area B | 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 | For mid-sized networks | 16 bits for the network and 16 for the host |
Area C | 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 | For small networks | 24 bits for the network and 8 for the host |
Internet providers assign each router a public IP address so that other routers and servers on the World Wide Web can accurately identify it. Unlike a private IP address, this must be a unique number.
In the table below, we've summarized the differences between both types of IP addresses:
Private IP address | Public IP address | |
|---|---|---|
Can be used on the WWW? | No | Yes |
Unique? | Not necessarily | Yes |
Can be seen with online tools? | No | Yes |
Changes with each Internet session? | Usually, no | Yes (private routers) No (servers) |
Free | Yes | No |
IPv4 vs. IPv6
An IPv4 IP address, like 35.246.185.33, can be displayed either in bits (32) or bytes (4). This means that there exist 2^32 or approximately 4.29 billion possible combinations. At first glance, this may seem like quite a lot, however, more than two decades ago, the number of publicly available IP addresses was starting to run out. For that reason, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) developed a new system.
Known as IPv6, these addresses are 128 bits long, allowing for 7.9 x 10^28 possible combinations. In other words, even if everyone on the planet had a billion devices each, it would take 10 Earths to exhaust the permutations. As such, the danger of running out of IP addresses in the near and distant future has gone away.
IPv6 IP addresses are written in hexadecimal form (base 16), consisting of numbers from 0-9, as well as the letters a-f. In order to make sense of the combinations, 16-bit (4-character) groups are separated by a semi-colon.
Static vs. Dynamic IP Addresses
Because a website's IP address doesn't usually change on its own, it's commonly referred to as a static IP address. Since they don't change, static IP addresses allow Internet users, as well as DNS services, to locate the resource that they're looking for without too much effort. Just think how frustrating it would be if your favorite restaurant or store had a new physical address every time you wanted to visit.
Most organizations and businesses prefer static IP addresses for this reason since they more readily facilitate remote access to Intranet resources. However, static IP addresses need to be purchased from an Internet provider and can be expensive. In addition, they make life easier for hackers, since the target's location doesn't change.
Generally, only routers and servers have public IP addresses.
On the other hand, individuals who connect to the Internet via a router are assigned a new IP address every session. Since these are automatically generated by a DHCP server, users don't have to take any action on their own. Cybercriminals also run into difficulties when IP addresses change so frequently.
Find an IP: On Your Own or With an Online Tool
It's easy to find out any device's IP address, regardless of whether it's a tablet, smartphone, or PC. The same goes for website IP addresses. Below, we'll show you how to do this.
See Your IP Address (Windows)
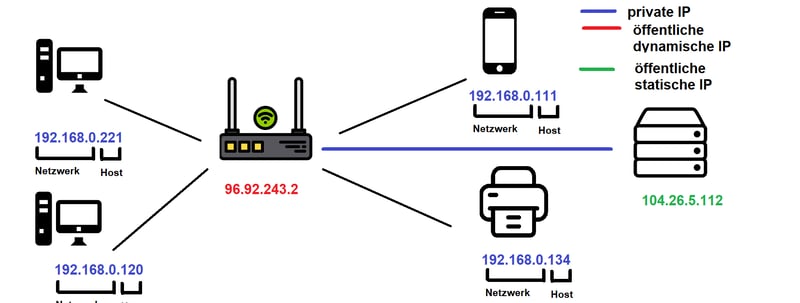
If using Windows, you can find out both your private and public IP addresses with the following steps:
- 1.
Open Command Prompt, either through the Windows Menu or by typing cmd.
- 2.
Type ipconfig and press enter.
- 3.
Look for entries with number and letter combinations like those in the IP address section above. The first of these shows your public IP address. If any privacy extensions are activated, Windows will generate a 64-bit number and replace the last 64 bits to better protect your privacy. Your private IP address will be displayed under Link-local IPv6 Address, with your IPv4 address appearing directly below it.
When using the ipconfig prompt, Windows lists all IP addresses on the system.
How to See Your IP Address (macOS)
Finding your IP address on a system running macOS is even easier than on Windows:
- 1.
Open system settings.
- 2.
Click on Network.
- 3.
All active connections will appear green. To view a device's IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, click on the connection they're using.
- 4.
Alternatively, you can open the Terminal, type ifconfig en0, and press enter.
Find Out Your IP on iOS
It's just as easy to find out what your IP address is on an iPhone as on macOS:
- 1.
Open settings.
- 2.
Tap Wi-Fi and select the network you're currently on.
- 3.
Tap on the blue "i" next to the network's name. Then, you'll see your device's private IP address.
Find Out Your IP on Android
If you have an Android smartphone or device follow these steps to find out its IP address:
- 1.
Go to Settings.
- 2.
Tap on Connections.
- 3.
Select WLAN. You should now be able to see all available WiFi connections.
- 4.
Find the network that you're connected to and open settings for it (tap on Configure along the bottom).
- 5.
Depending on your phone's model, the interface can vary but look for IP Address among the options. There, you'll be able to see both your public and private IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses.
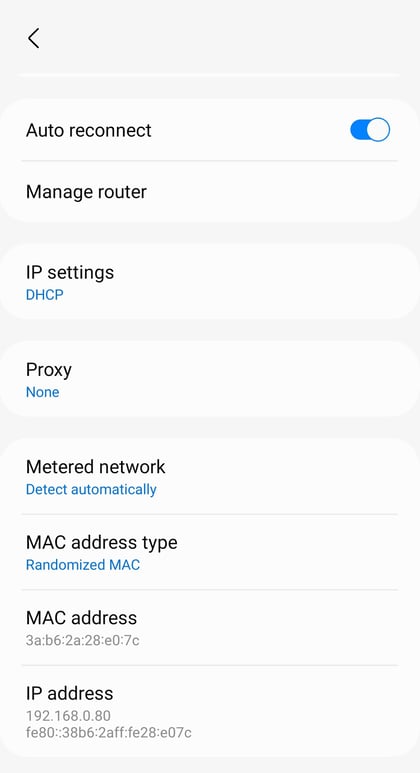
View your private IP address in the WLAN area of your Android device's Settings menu.
Online Tools That Show Your IP Address
If you only want to find out what your public IP address is, you can on websites like Whatismyipaddress.com. Internet Tools such as Ipinfo can show you a domain's IP address or server location, such as those for EXPERTE.com or bbc.co.uk.
Is an IP Address a Security Risk?
Back in 2010 Eric Schmidt, then CEO of Google, said: "We know where you are. We know where you were. We know, more or less, what you think." It's no secret that search engines, Internet providers, and websites track users by their IP addresses, cookies, or social media profiles. Even though this is distressing, your IP address is actually more important owing to what it reveals about your physical location.
No one is going to knock on your door, however, things like your ZIP code and what neighborhood you're living in can be determined from it. This isn't all bad either, since you'll get accurate weather forecasts, or ads from new restaurants close by. This can feel like an invasion of your privacy since strangers will have more information about you than you might have been willing to offer up.
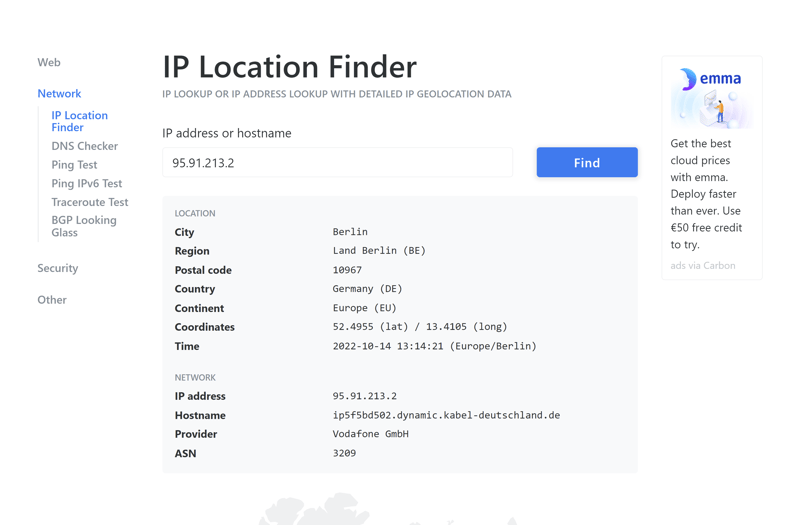
Sites that you visit will know which city or town you're in and can even find out your ZIP code.
Through phishing or data leaks, cybercriminals can also find out your IP address. Hackers often collect IP addresses and then use them for IP spoofing. This occurs when they conceal their real IP address to launch DDoS attacks using stolen or compromised IPs from unsuspecting victims. Anyone who wants to stay ahead of online threats has plenty of reasons to safeguard their IP address.
Why Should I Hide My IP Address?
Most people don't mind legitimate businesses and corporations prying into their lives for marketing purposes. However, if this makes you uncomfortable, hiding your IP address is one of the first steps you can take to protect your online privacy.
Another good reason to conceal your IP address is that it allows you to bypass geoblocking or regional restrictions. If you've ever been unable to access or watch content because of where you physically are, you know how frustrating this can be. By taking on a different IP address, you can watch British or German Netflix and check out shows or movies that might not be part of your local catalog. All that's needed is a new IP address.

Content is often limited to particular jurisdictions owing to the licensing agreements.
Should you be visiting a country like China, where the Web is heavily censored and social media like Facebook and Instagram are usually blocked, you'll quickly want to find a way to get back on the "real" Internet. The only option for breaking through the Great Firewall is to hide your IP with a VPN, Tor, or a proxy server. In the next section, we'll let you know what the advantages and disadvantages of each option are.
Even though Google and other services won't be able to see your IP address, they can still collect information about you. They'll know which operating system, hardware, browser, and plugins you're using. Taken together, these can create an incredibly accurate mosaic of who you are, even without your IP address. Total anonymity might not be possible online, but, there are ways to make browser fingerprinting difficult for third parties.
How Can I Hide My IP Address?
There are several ways to change your IP address, such as:
VPNs act as an intermediary between your router and the resource you're attempting to visit. Each request is encrypted before being sent to your VPN provider's server. From there, it's forwarded to the target server, albeit, with the VPN's IP address. Since VPNs operate servers around the world, you can choose from dozens of countries to connect to. The only downside is that most VPN services require paid subscriptions.
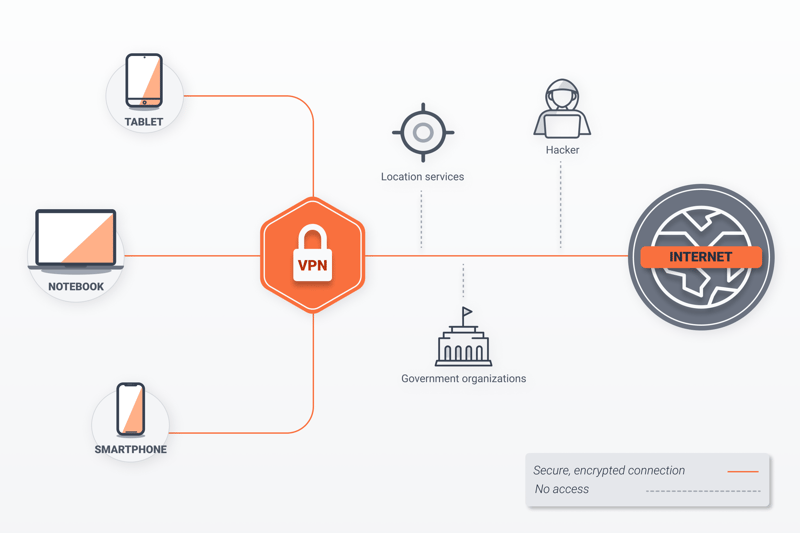
With a VPN you can hide your IP address with a few clicks.
The Onion Router or Tor is a worldwide computer network, each of which acts as a node. Here too, your target will only see the last Tor node's IP address. Since Tor is volunteer-based and free to use, the hardware contributed by participants isn't the latest and greatest. In addition, your requests will be routed through multiple nodes, impacting speed more than with VPNs.
Proxy services, like VPNs, act as intermediaries between your router and the server of whatever website or resource you're trying to visit. However, unlike a VPN, proxy connections usually don't encrypt your requests, and speeds vary considerably from server to server. There are premium proxy services that encrypt all requests and traffic and are both faster and more reliable than their free counterparts.
Conclusion
An IP address identifies any Internet-capable device. Along with private IP addresses, which only play a role within a network, public IP addresses facilitate Internet communication between routers and servers. While the former have dynamic IP addresses that constantly change, the latter relies on static or permanent addresses.
When surfing the Web websites that you visit will see your IP address. With these, businesses can determine where you're physically located, making it possible to target you with personalized ads. However, cybercriminals can misuse IP addresses. Should you want to protect yourself, solutions like VPNs, proxy services, or Tor are all capable of hiding your IP address and bypassing regional content restrictions.
Even when you hide your IP address with one of the above, search engines, apps, and marketing companies will be able to track you. To be as anonymous online as possible, you'll have to embrace some additional measures. These include so-called privacy browsers, or limiting your usage of apps and social media. Whatever steps you take, remember that there's no such thing as 100% anonymity.
FAQs
An IP address is a combination of characters that acts like a telephone number, uniquely identifying a device on a network. It's important to distinguish between public and private IP addresses; the former are used on the World Wide Web and are only assigned once, whereas the latter are assigned by networks.
IPs make it possible for devices to communicate with one another on the Internet. Each router is assigned an IP address by the Internet provider. Whenever a request comes from this router, the target server knows where to send the requested data package.
Static IP addresses don't change, which helps explain why they're used by servers and businesses. Regular users, on the other hand, are assigned a new IP address every session. In this case, the IP address is said to be dynamic.
Cybercriminals often gain access to IP addresses by hacking the servers that these are saved on. After that, it's likely that they'll be misused for DDoS attacks (so-called IP spoofing).